You have seen the basic structure of a C program, so it will be easy to understand other basic building blocks of the C programming language. A C program consists of various tokens and a token is either a keyword, an identifier, a constant, a string literal, or a symbol. For example, the following C statement consists of five. Enter a number: -5 This statement is always executed. C if.else The if else executes the codes inside the body of if statement if the test expression is true and skips the codes inside the body of else.
C Basic Syntax In the previous post, you learned to create simple Hello World program in C by using Notepad or Dev-C editor. This tutorial teaches you the basic syntax of C programming language that you should know since you are new to this computer programming language. Summary of basic C-commands Compiling To compile a C-program, you can use either gor c. G -oexecutable filename.out sourcefilename.cc c -oexecutable filename.out sourcefilename.cc e.g. G -o Csampleinout.out Csampleinout.cc For the following commands you can find at the end of this summary sample programs. Programming with the Dev C IDE 1 Introduction to the IDE Dev-C is a full-featured Integrated Development Environment (IDE) for the C/C programming language. As similar IDEs, it offers to the programmer a simple and unified tool to edit, compile, link, and debug programs. It also provides support for the management of the.
Originally released by Bloodshed Software, but abandoned in 2006, it has recently been forked by Orwell, including a choice of more recent compilers. It can be downloaded from:
http://orwelldevcpp.blogspot.comInstallation
Run the downloaded executable file, and follow its instructions. The default options are fine.Support for C++11
By default, support for the most recent version of C++ is not enabled. It shall be explicitly enabled by going to:Tools -> Compiler OptionsHere, select the 'Settings' tab, and within it, the 'Code Generation' tab. There, in 'Language standard (-std)' select 'ISO C++ 11':
Ok that. You are now ready to compile C++11!
Compiling console applications
To compile and run simple console applications such as those used as examples in these tutorials it is enough with opening the file with Dev-C++ and hitF11.As an example, try:
File -> New -> Source File (or Ctrl+N)There, write the following:
Then:
File -> Save As... (or Ctrl+Alt+S)And save it with some file name with a
.cpp extension, such as example.cpp.Now, hitting
F11 should compile and run the program.If you get an error on the type of
x, the compiler does not understand the new meaning given to auto since C++11. Please, make sure you downloaded the latest version as linked above, and that you enabled the compiler options to compile C++11 as described above.Tutorial
You are now ready to begin the language tutorial: click here!.C++ language is a direct descendant of C programming language with additional features such as type checking, object oriented programming, exception handling etc. You can call it a “better C”. It was developed by Bjarne Stroustrup.
C++ is a general purpose language language, when I say general purpose it simply means that it is designed to be used for developing applications in a wide variety of domains.
C++ Tutorial
To learn C++ programming, refer these tutorials in the given order. These tutorials are written for beginners so even if you have no prior knowledge in C++, you won’t face any difficulty understanding these tutorials.
Basics
1. First C++ Program – Hello World!
2. Variables and their types
3. Data types
4. Operators in C++
Control Statements
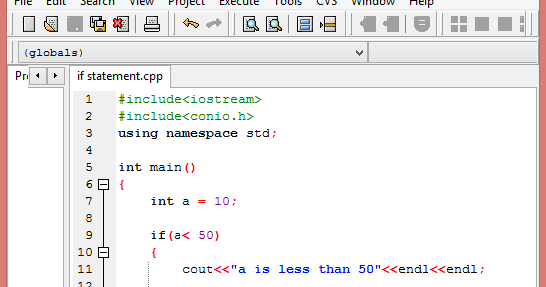
5. If, if..else-if statement
6. Switch Case in C++
7. For loop
8. while loop
9. do while loop
10. Continue statement
11. Break statement
12. goto statement
Functions
13. Functions in C++
14. Default arguments in Functions
15. C++ Recursion
Arrays
16. Arrays
17. Multidimensional arrays
18. Passing Array to function
19. C++ Strings
Pointers
20. Pointers in C++
21. this Pointer
OOPs
22. OOPs Concepts
23. Constructor
24. Destructor
25. Structure
26. How to pass and return struct from function
27. Enumeration
28. Inheritance
29. Polymorphism
30. Function Overloading
31. Function Overriding
32. Virtual Function: Run time Polymorphism
33. Encapsulation
34. Abstraction
35. Interfaces – Abstract class
36. Pass and return object from function
37. Friend class and friend Function

Features of C++
Function Syntax In C
1) Better memory management – you can dynamically allocate memory during runtime using new and delete operator in C++ to have better memory management.
2) Object oriented – C++ supports object oriented programming features, which means we can use the popular OOPs concepts such as Abstraction, Inheritance, Encapsulation and Inheritance in C++ programs, these features make writing code in C++ a lot easier. We will cover them in detail in this tutorial series.
3) Portable – Most of C++ compilers supports ANSI standards that makes C++ portable because the code you write on one operating system can be run on other Operating system without making any change. We cannot say C++ a fully platform independent language as certain things in C++ are not portable, such as drawing graphics on a screen, since standard C++ has no graphics or GUI API.
4) Structured programming language – We have functions in C++, which makes easier to break a problem into small blocks of code and structure the program in such a way so that it improves readability and reusability.
C++ Method Syntax
5) Exception handling: Just like Java we can do exception handling in C++ which makes it easier to identify and handle the exceptions.
6) Simple – Last but not least, just like C, it is easier to write a program in C++. Once you get familiar with the syntax of C++ programming language, it becomes a lot easier to code in C++.